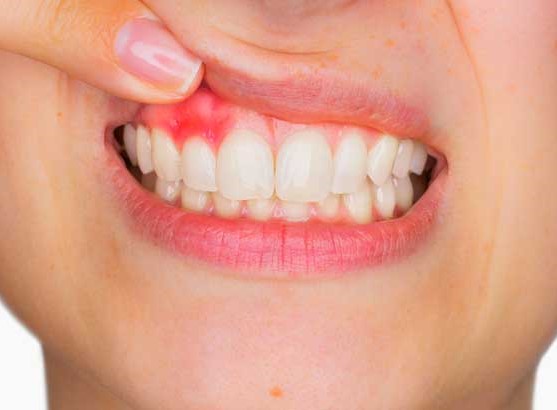
Causes and treatment of gingivitis

Dental Health and Your Child’s Teeth
July 18, 2018
Is Tooth Paint Effective For Whitening Teeth?
August 2, 2018Gingivitis means inflammation of the gums, or gingiva. It commonly occurs because a film of plaque, or bacteria, accumulates on the teeth. Gingivitis is a non-destructive type of periodontal disease, but untreated gingivitis can progress to periodontitis. This is more serious and can eventually lead to loss of teeth.
Gingivitis often resolves with good oral hygiene, such as longer and more frequent brushing, and flossing. In addition, an antiseptic mouthwash may help.
In mild cases of gingivitis, patients may not even know they have it, because symptoms are mild. However, the condition should be taken seriously and addressed immediately.
Causes
The most common cause of gingivitis is the accumulation of bacterial plaque between and around the teeth. The plaque triggers an immune response, which, in turn, can eventually lead to the destruction of gingival, or gum, tissue. It may also, eventually, lead to further complications, including the loss of teeth.
Other causes and risk factors
- Changes in hormones: This may occur during puberty, menopause, the menstrual cycle, and pregnancy
- Some diseases: Cancer, diabetes, and HIV
- Drugs, smoking, age and poor diet
For the emergence and development of inflammation, a genuine factor also plays an important role.
Signs and symptoms of gingivitis might include:
- bright red or purple gums
- tender gums that may be painful to the touch
- bleeding from the gums when brushing or flossing
- halitosis, or bad breath
- inflammation, or swollen gums
- receding gums
- soft gums
Treatment
If diagnosis happens early, and if treatment is prompt and proper, gingivitis can be successfully reversed.Treatment involves care by a dental professional, and follow-up procedures carried out by the patient at home.The dental professional will explain the importance of oral hygiene and how to brush and floss effectively.Follow-up appointments may be recommended, with more frequent cleanings if necessary.
Everyday care
- brush teeth at least twice a day.
- use an electric toothbrush
- floss teeth at least once a day
- regularly rinse mouth with an antiseptic mouthwash
- A dentist can recommend a suitable brush and mouthwash.